

The output of that should look like the one below. Luckily, this can be done quickly and efficiently. You’ll probably want to do the same after you add a Git remote repository. You will have to add the URL of your own repository.Įveryone who works in the IT industry wants to check if something that was done actually works. Please take note that “origin” can be named to whatever you prefer and the URL that we used is just an example. In order to add the remote repo, use the syntax below: git remote add origin URL will be generated after you create a remote repository on GitHub. Name for your remote and URL of the remote repository. Let’s see how we can add a Git remote repository. You can name your remote connection however you want, but “origin” is a commonly agreed term when it comes to repository naming. That is just the term to name your remote connection.
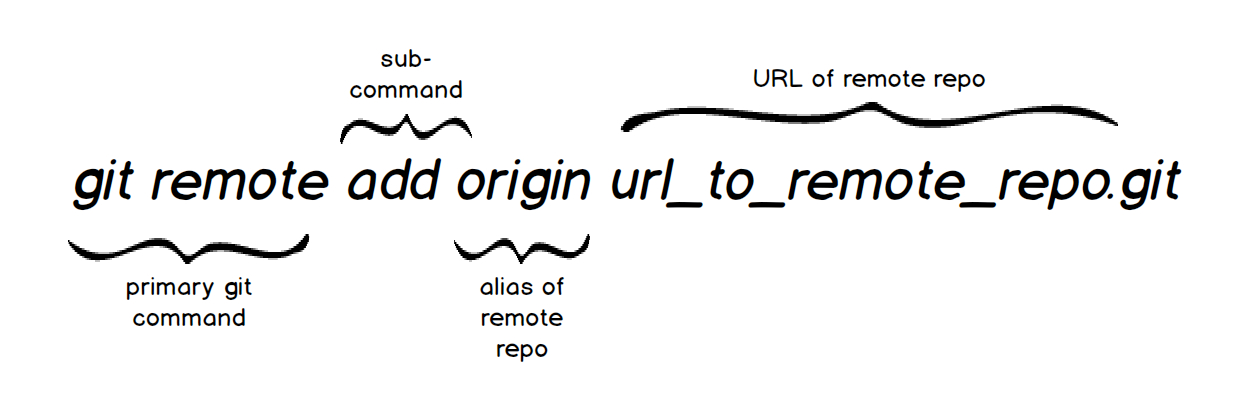
Origin is not a flag nor does it have to be called “origin” in the first place. You will notice word origin In an example of the syntax that you see below. Next, add any files in the folder to the first commit using the following commands: > git add -all.
#Git add remote repository to existing code
From the command line, navigate to the root folder containing the code and run. But what if you created a local copy first? In that case, you will have to add a Git remote repository. Use the git init command to create a new repo from an existing folder on the computer. Local copy that was created this way will be automatically connected to the remote repo. This means that you will have a local copy of the Git repository tied to your project. you can use any name instead of "origin".Every time you clone a Git repository, you are actually downloading your project locally. "origin" is the local name of the remote repository. Note: "origin" is a convention not part of the command. You can verify that the remote URL has changed, with command git remote -v.

For example, origin or upstream are two common choices.įor example you can change your remote's URL from SSH to HTTPS with the git remote set-url command. The git remote set-url command takes two arguments: The git remote set-url command changes an existing remote repository URL. The git remote add command takes two arguments: This command is used to add a new remote, you can use this command on the terminal, in the directory of your repository. git then the repository not exists, so you have to add origin with command git remote add You can check remote with command git remote -v it will show remote url after name, or if this command gives error like fatal: Not a git repository (or any of the parent directories). So the command git remote set-url will only work if you've either cloned the repository or manually added a remote called origin. Unfortunately, the instructions offered by Github on an empty repo’s URL don’t always work out smoothly. This is a useful workflow for local projects in need of remote versioning. You can not call remote set-url origin just after git init, Because the git remote set-url command will not create origin, but it changes an existing remote repository URL. Adding a local project to an empty repository on Github is an easy process. To know about the list of all branches you have in your repository type : git branch This command simply pushes your files to the remote repository.Git has a concept of something known as a "branch", so by default everything is pushed to the master branch unless explicitly specified an alternate branch. git remote set-url origin command means that if at any stage you wish to change the location of your repository(i.e if you made a mistake while adding the remote path using the git add command) the first time, you can easily go back & "reset(update) your current remote repository path" by using the above command. To verify that the remote is set properly type : git remote -vĢ.Here origin is an alias/alternate name for your remote repository so that you don't have to type the entire path for remote every time and henceforth you are declaring that you will use this name(origin) to refer to your remote.
• Your remote repository could be anywhere on github, gitlab, bitbucket, etc. Make sure you are in /devops directory Add remote to your existing repository using : git remote add origin :#Git add remote repository to existing series
git remote add origin This command is the second step in the command series after you initialize git into your current working repository using git init.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
